Brushless Motor Working Principle and Structure
Brushless motor structure and composition
The brushless motor's core structure consists of an inversely mounted conventional direct current (DC) motor. Its armature is positioned on the stator while the permanent magnetic poles are located on the rotor, resembling the design of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. Each phase winding is linked to an external electronic switching circuit. Within this circuit, the switching transistors are controlled by signals from the position sensor. The motor body depicted in the "Structural Diagram of Brushless Motor" is three-phase and two-pole design. The three-phase stator windings are individually connected to the corresponding power switch devices in the electronic switch circuit. In the diagram, the A-phase, B-phase, and C-phase windings connected to the power switching transistors VT1, VT2, and VT3, respectively. The position sensor is linked to the motor shaft. When one phase of the stator winding is energized, the current interacts with the magnetic field produced by the rotor's permanent magnets to generate torque, driving the rotor to rotate. This movement is converted into an electrical signal by the position sensor, which controls the electronic switching circuit. Consequently, the stator windings are sequentially activated, ensuring that the phase current of the stator adjusts in sync with the rotor's position. The sequencing in the electronic switching circuit, synchronized with the rotor's angular movement, effectively replaces the function of a mechanical commutator. Therefore, from a structural perspective, the brushless motor can be considered a 'motor system' comprised of an electronic switching circuit, a permanent magnet synchronous motor, and a position sensor.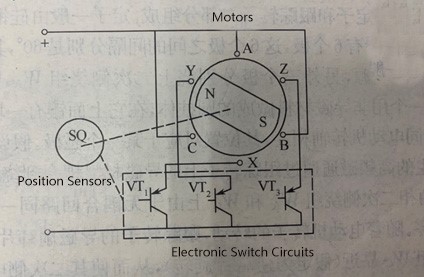 Structural diagram of brushless motor
Structural diagram of brushless motor 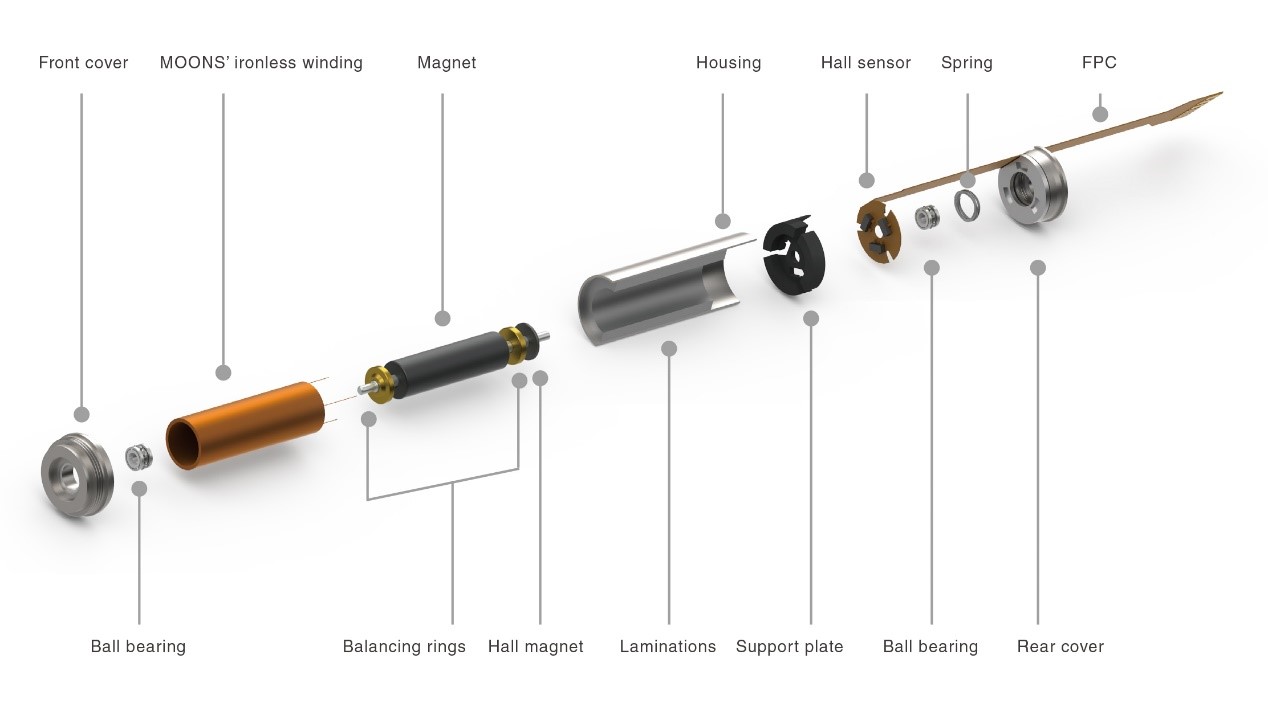 ECU series brushless motor product structure diagram
ECU series brushless motor product structure diagram Brushless Motor Working Principle
The working principle of brushless motor involves the interaction between the electromagnetic field and motor components, which generates the necessary power for the motor to operate. The principal components include the rotor, the stator, and the electronic speed controller. The stator is the stationary component of the motor, composed of a series of electromagnets that are arranged in a specific pattern, commonly referred to as stator windings. The number and configuration of these stator windings play a crucial role in determining the speed, torque, and direction of the brushless motor. They are also essential for generating the rotating magnetic field. These windings are connected to a DC power supply and are energized in a specific sequence under the control of an electronic controller. The rotor is the dynamic component of the brushless motor, tasked with generating mechanical power. It is a complex and precision-engineered part, primarily made up of permanent magnets organized in a specific pattern to establish a series of north and south poles. These magnets are encircled by the stator windings. The stator windings are energized in a specific sequence to generate a rotating magnetic field, which interacts with the permanent magnets on the rotor to rotate the rotor, thereby generating mechanical power for the brushless motor.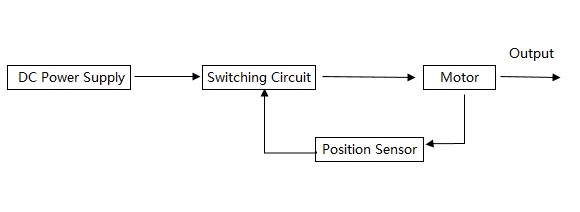 Brushless motor working principle block diagram From the above discussion, it is evident that the brushless DC motor system comprises three main components: the motor, the rotor position sensor, and the switching circuit. The block diagram illustrating the working principle of the brushless motor is depicted in the figure. The DC power supply feeds the motor via the switching circuit. The position sensor continuously monitors the rotor's position and controls the activation and deactivation of the switching transistors based on the rotor's position signals, thus facilitating brushless commutation. Application of brushless motor 1. Computer Peripherals and Office Automation: Brushless motors are utilized in printers, floppy disk drives, hard disk drives, optical disk drives, fax machines, and copiers, etc. 2. Household Appliances: Brushless motors are used in audio-visual equipment, household washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioning systems. 3. Industrial Drive and Servo Control: Brushless motors are integral to CNC machine tools, modular machine tools, textile machinery, printing machinery, loading, and unloading machinery, metallurgical machinery, postal machinery, automated production lines, and various specialty machines. 4. Transportation: Application in vehicles such as automobiles, electric cars, electric motorcycles, and electric bicycles. 5. Medical Field: Brushless motors are found in high-speed centrifuges, high-speed dental and surgical instruments, and heart pumps, etc. Additionally, brushless motors are employed to enhance system reliability in special environmental conditions, such as areas with moisture, vacuums, or harmful substances. The military and aerospace industries were among the first to adopt brushless motors for their advanced applications.
Brushless motor working principle block diagram From the above discussion, it is evident that the brushless DC motor system comprises three main components: the motor, the rotor position sensor, and the switching circuit. The block diagram illustrating the working principle of the brushless motor is depicted in the figure. The DC power supply feeds the motor via the switching circuit. The position sensor continuously monitors the rotor's position and controls the activation and deactivation of the switching transistors based on the rotor's position signals, thus facilitating brushless commutation. Application of brushless motor 1. Computer Peripherals and Office Automation: Brushless motors are utilized in printers, floppy disk drives, hard disk drives, optical disk drives, fax machines, and copiers, etc. 2. Household Appliances: Brushless motors are used in audio-visual equipment, household washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioning systems. 3. Industrial Drive and Servo Control: Brushless motors are integral to CNC machine tools, modular machine tools, textile machinery, printing machinery, loading, and unloading machinery, metallurgical machinery, postal machinery, automated production lines, and various specialty machines. 4. Transportation: Application in vehicles such as automobiles, electric cars, electric motorcycles, and electric bicycles. 5. Medical Field: Brushless motors are found in high-speed centrifuges, high-speed dental and surgical instruments, and heart pumps, etc. Additionally, brushless motors are employed to enhance system reliability in special environmental conditions, such as areas with moisture, vacuums, or harmful substances. The military and aerospace industries were among the first to adopt brushless motors for their advanced applications. 