How to Connect Stepper Motor to Your Drive
• 2-PHASE MOTORS
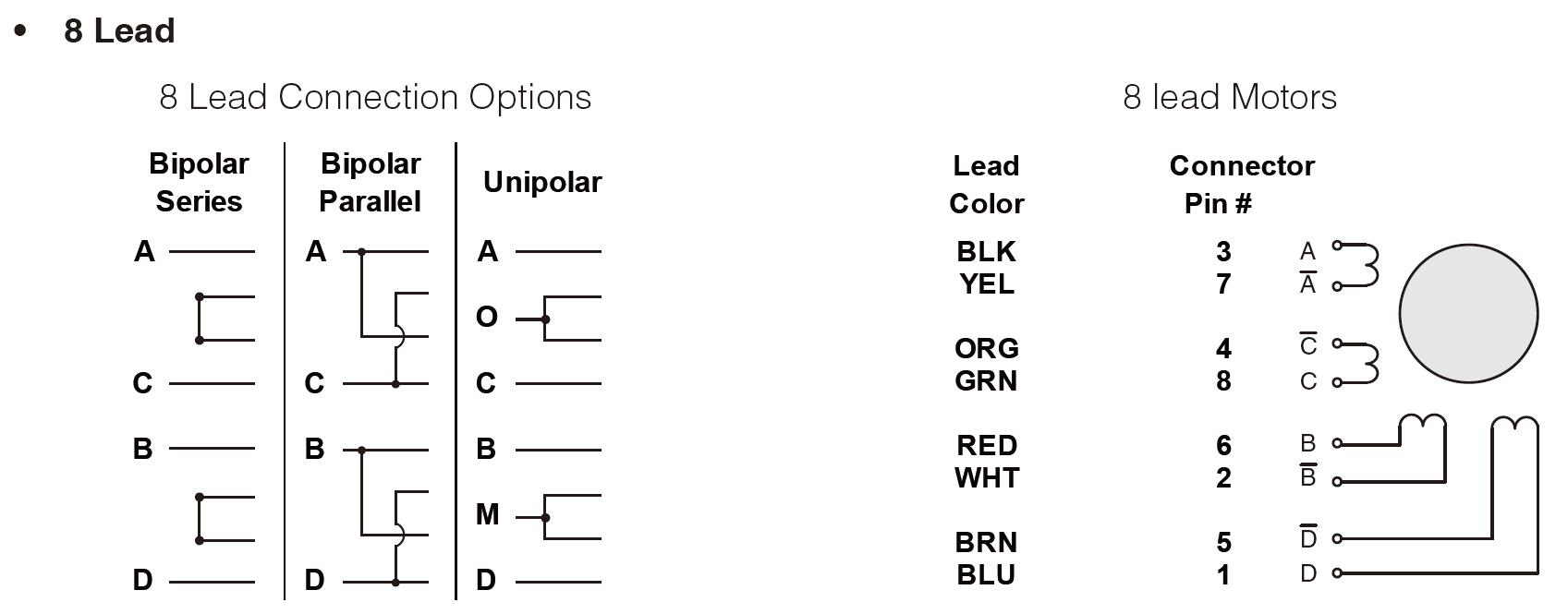
A typical driving pattern for a bipolar stepper motor with two coils would be A+ B+ A- B-. In other words, drive coil A with positive current, then remove current from coil A; then drive coil B with positive current, then remove current from coil B; then drive coil A with negative current, then remove current from coil A; then drive coil B with the negative current; the cycle is complete.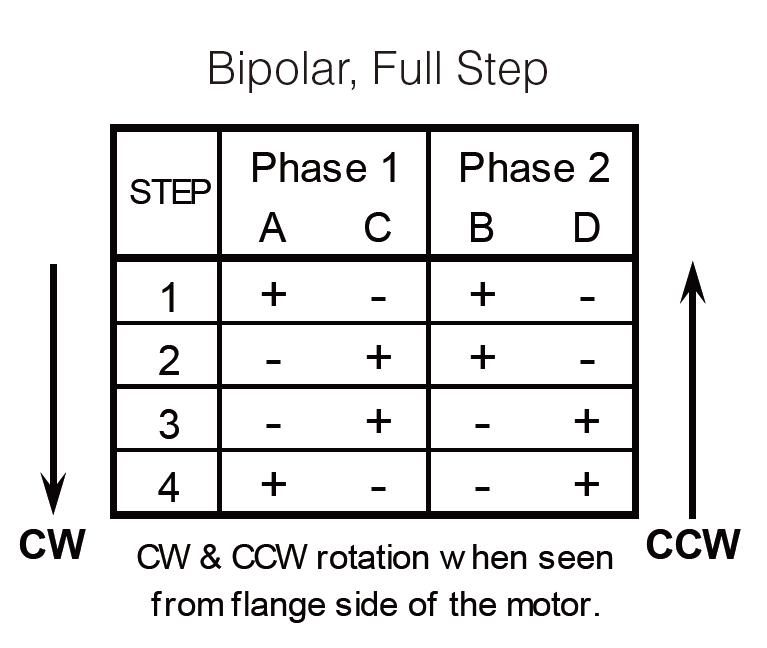 A bipolar motor has a single winding per phase. In order to reverse a magnetic pole, the current in a winding must be reversed, so a driving circuit must be more complex, typically one using an H-bridge (an H bridge is an electronic circuit that switches the polarity of a voltage applied to a load). These circuits are commonly used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards or backward.) arrangement. Each phase has two leads, none of which are common.
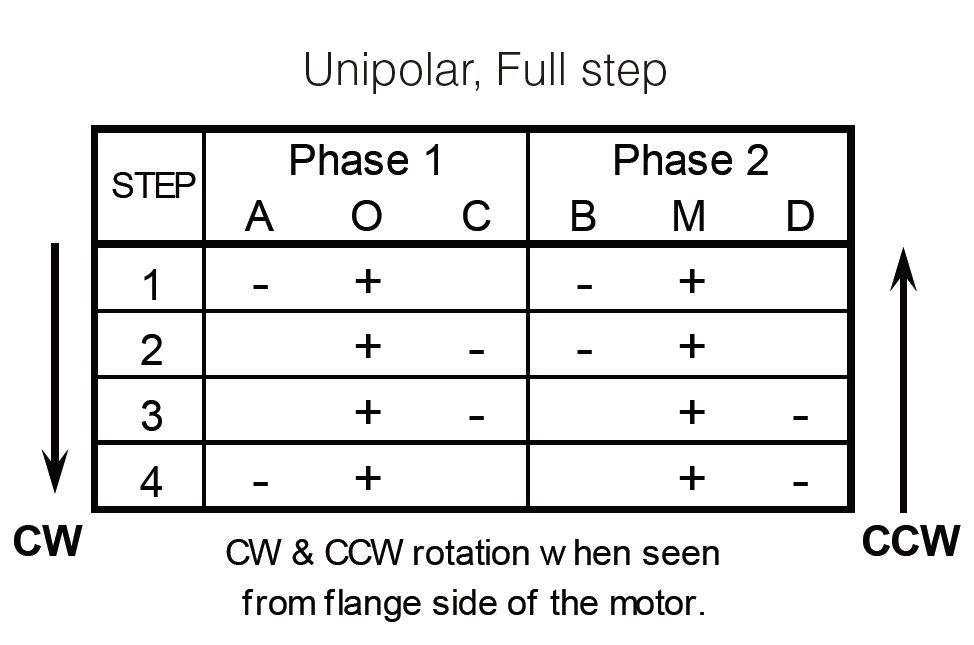
A bipolar motor has a single winding per phase. In order to reverse a magnetic pole, the current in a winding must be reversed, so a driving circuit must be more complex, typically one using an H-bridge (an H bridge is an electronic circuit that switches the polarity of a voltage applied to a load). These circuits are commonly used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards or backward.) arrangement. Each phase has two leads, none of which are common. 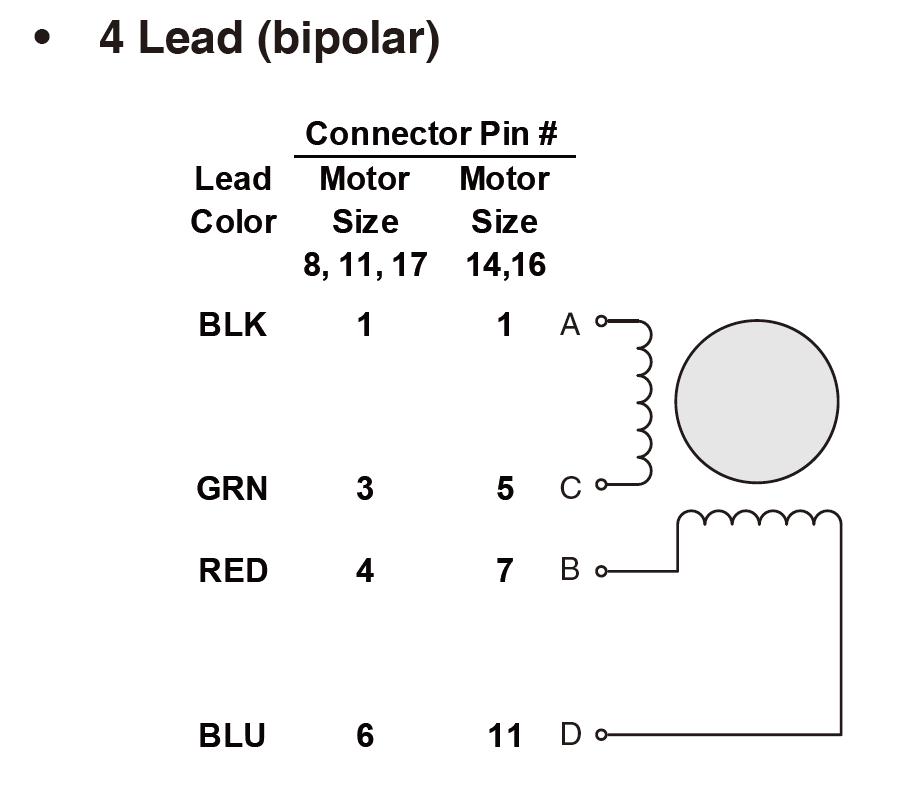 The unipolar stepper motor has one winding with a center tap for each phase. The windings are switched on for each direction of the magnetic field. Using this arrangement, a magnetic pole can be reversed without changing the direction of the current, allowing the commutation circuit to be very simple (e.g., a single transistor for each winding). For a typical two-phase motor, the center tap of each winding is made common, resulting in three leads per phase. It is common for these two-phase commons to be internally coupled so that the motor has only five leads.
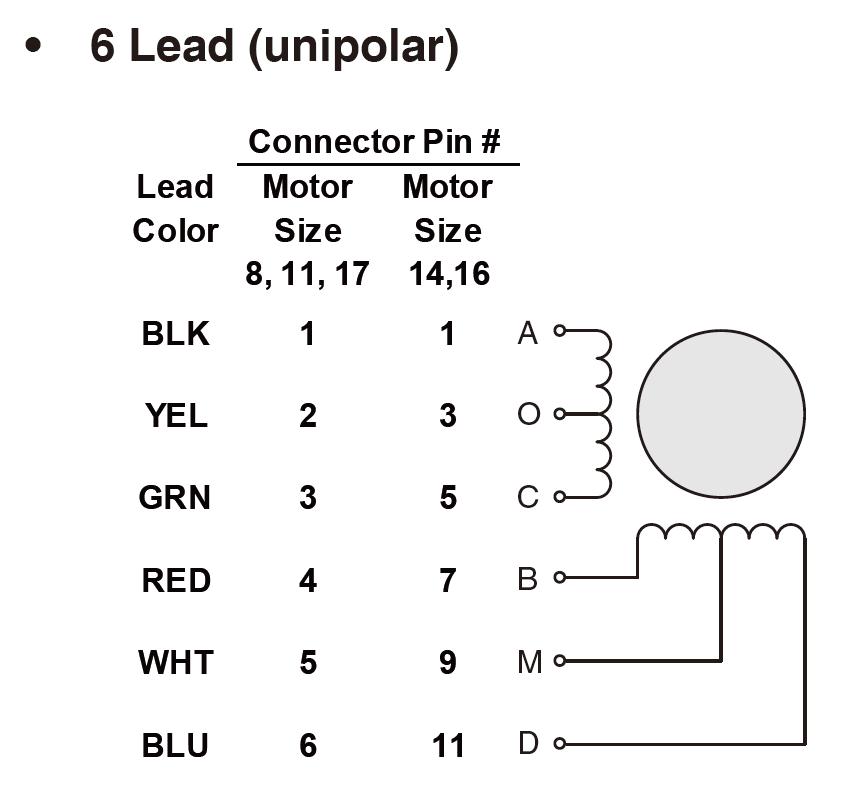
The unipolar stepper motor has one winding with a center tap for each phase. The windings are switched on for each direction of the magnetic field. Using this arrangement, a magnetic pole can be reversed without changing the direction of the current, allowing the commutation circuit to be very simple (e.g., a single transistor for each winding). For a typical two-phase motor, the center tap of each winding is made common, resulting in three leads per phase. It is common for these two-phase commons to be internally coupled so that the motor has only five leads.