How to Control HB Stepper Motors?
Stepper Motor Category
MOONS' offers a variety of stepper motor types including the basic type, encoder type, IP65 type, Integrated type with drive and controller, brake type, and geared type. We can also provide customized combinations to optimize compactness in motion control units. For example, MOONS' can supply motors with both a gearbox and encoder, or an IP65-rated integrated motor with drive, controller, and encoder. All combinations are available upon request to meet specific customer needs.| • Standard Hybrid Stepper Motors The basic model is user-friendly and features a well-balanced design of functions and characteristics, meeting the needs of most applications. |  |
| • Encoder Hybrid Stepper Motors The encoder-type stepper motor enables closed-loop control, allowing encoder feedback signals to be used for position verification, as well as for functions like stall detection and step-loss compensation, depending on the drive's features. |  |
| • IP65 Hybrid Stepper Motors IP65-rated stepper motors, featuring dustproofing and resistance to low-pressure water jets, are ideal for use in wet industrial environments, such as in the food and beverage industry or for outdoor applications. The IP65 rating specifies that the motor is dust-tight (completely preventing dust ingress and ensuring full contact protection) and protected against water jets (water projected by a nozzle from any direction will not have harmful effects). |  |
| • Integrated Type with Drive and Controller Compared to separate motor and driver setups, integrated stepper motors offer a compact design that reduces system wiring, as well as installation and maintenance costs. For products with built-in controllers, only the power cord, essential communication lines, and sensor signals need to be connected. The distributed motion control functionality significantly reduces controller costs and simplifies the process of build complex systems. |  |
| • Brake Hybrid Stepper Motors This motor is equipped with a power-off electromagnetic brake. In the event of a power outage or other unexpected power loss, the brake holds the load in its current position, preventing it from falling or shifting. Brake-type stepper motors are widely used in vertical axis applications. |  |
| • Gearbox type stepper motor To maximize the motor's high controllability, a high-precision planetary gearbox is installed. The gearbox ensures accurate and smooth operation, even in applications that demand high torque. |  |
Control Modes for Drives
MOONS' advanced stepper drive technology allows each stepper motor to operate under various control modes. Such as pulse control, analog control, or program-resident modes. MOONS' stepper drives support a wide range of control signals, including digital and analog inputs, as well as various industrial fieldbus network protocols. MOONS' unique Q-programmable drives enable complex single-axis motion control by executing stored programs, allowing for sophisticated standalone operation.• Pulse Control
Pulse control is a traditional method for controlling the position and speed of a stepper motor. The rotation distance is proportional to the number of pulses, and the speed is proportional to the pulse frequency.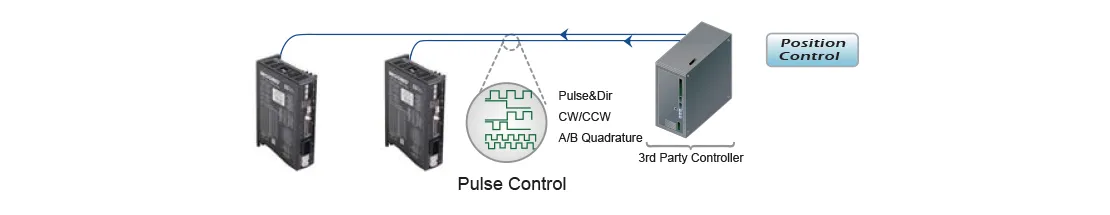 Three most popular pulse control digital signal types are Pulse & Direction, CW/CCW Pulse and A/B Quadrature.
Three most popular pulse control digital signal types are Pulse & Direction, CW/CCW Pulse and A/B Quadrature. | • Pulse & Direction By default, when the Pulse input transitions from high to low (falling edge) and the DIR input is set to low (or left floating), the motor rotates one step in the clockwise direction. When the Pulse input transitions from high to low (falling edge) and the DIR input is set to high, the motor rotates one step in the counterclockwise direction. *The direction of the DIR input can be configured using MOONS' software. The chart below shows the motor configuration where, with the DIR input set to ON, the motor rotates in the clockwise direction. | 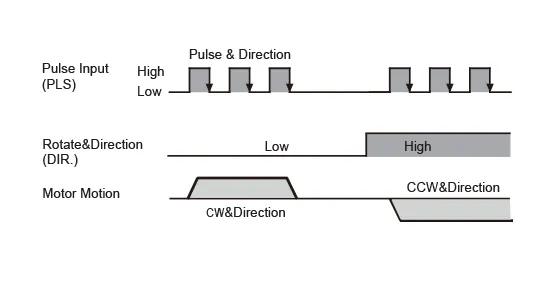 |
| • CW/CCW Pulse By default, when the CW pulse input transitions from high to low (falling edge) and the CCW pulse input is low (or left floating), the motor rotates one step in the clockwise direction. Similarly, by default, when the CCW pulse input transitions from high to low (falling edge) and the CW pulse input is low (or left floating), the motor rotates one step in the counterclockwise direction. *The direction settings can be configured via MOONS' software. The chart below shows the motor configured such that when the X1 input is ON, the motor rotates one step in the clockwise direction. | 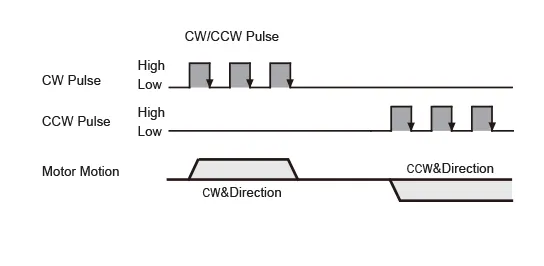 |
| • A & B Quadrature The motor rotates according to signals sent to the drive from a dual-channel incremental master encoder. The direction definition can be configured via MOONS' software, with the rotation direction determined by which channel leads the other. The chart below shows motor configured to rotate clockwise when input A leads input B. | 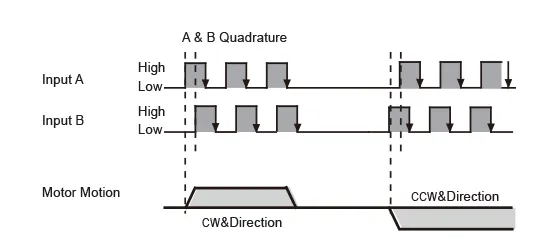 |
• Analog Control
MOONS' stepper drives support speed and position control based on analog signals, and step-servo models also support torque control using analog signals.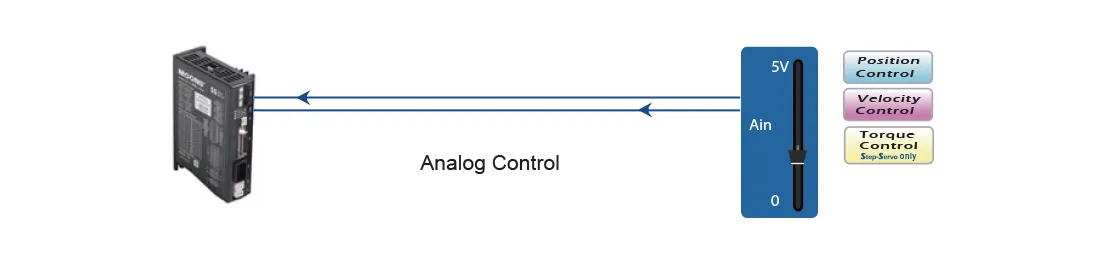
• Field Bus Control
MOONS' stepper drive supports all popular Industrial network communications including RS-485, Modbus, CAN and Ethernet.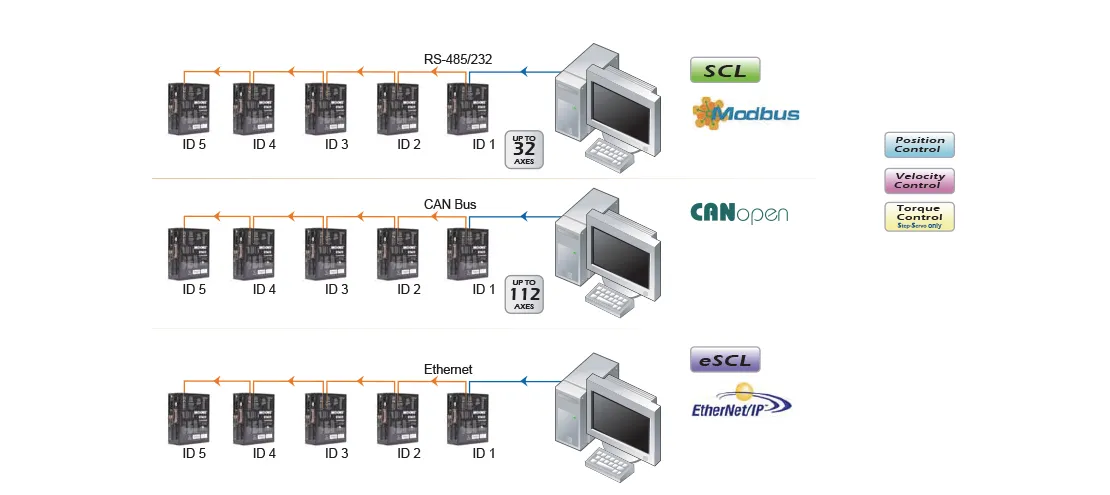
• Stand Alone Operation
MOONS' unique Q-programmable drives enable standalone single-axis motion control through stored program execution. Each Q drive can run up to 744 lines of stored Q program instructions in non-volatile memory. Programs are created using Q Programmer software, which offers multi-tasking capabilities, mathematical calculations using analog and digital parameters, conditional processing, data register manipulation, and more— all within a robust yet simple text-based programming language.
