How to Select a Better Extruder Stepper Motor for Your 3D Printers?
Extruders are used in FDM or FFF technology 3D printers, which are well known to all who work in the field. In the extruder, the stepper motor is responsible for feeding the filament and controlling the movement of the filament in the hot end. Once the filament is melted in the hot end, a thin thread of plastic is extruded out of the nozzle of the hot end.  Stepper motor can affect printing quality in a number of ways. ● Holding torque
Stepper motor can affect printing quality in a number of ways. ● Holding torque
● Resolution
● Step Accuracy
● Temperature rise
● Vibration Holding torque – normally, stepper motors with higher holding torque have a higher working torque at low speed. Having a higher working torque can ensure sufficient power to pull the filament spool and feed the filament without delay into the extruder. Holding torque – it can lock the position of the extruder during intervals of the printing process. The higher the holding torque, the less likely it is that a small gap will appear at the start of each layer of the print. Obtaining a stepper motor with a higher holding torque is not difficult. Several stepper motors have higher holding torque, but they achieve this by increasing the motor size or increasing the current. A larger motor size will result in a larger extruder, and a higher current will result in a higher temperature rise in the clod end, which requires more cooling capacity. MOONS' brand differs from other brands in the following ways:
Obtaining a stepper motor with a higher holding torque is not difficult. Several stepper motors have higher holding torque, but they achieve this by increasing the motor size or increasing the current. A larger motor size will result in a larger extruder, and a higher current will result in a higher temperature rise in the clod end, which requires more cooling capacity. MOONS' brand differs from other brands in the following ways: 
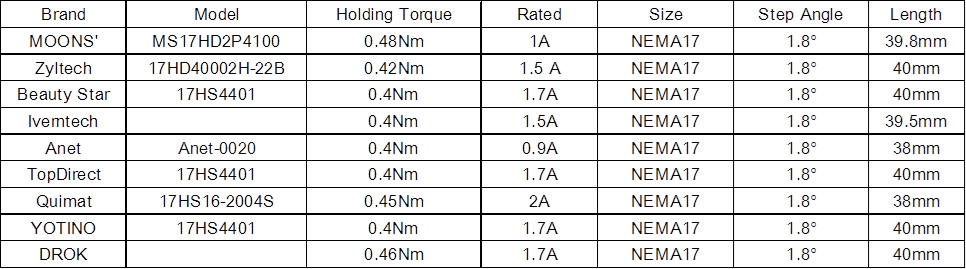 MOONS' MS17HD2P4100 has a holding torque of 0.48Nm at a motor size of NEMA17, which requires a lower-rated current. Resolution – resolution means the minimum turning angle that a stepper motor can reach, which is called Step-Angle. The most commonly used Step angles are 1.8 degrees and 0.9 degrees. In order to improve resolution, micro-step can be used with a micro-step driver. Micro-stepping refers to the ability to control filament movement in very small increments, thus improving the quality of printing. Step Accuracy — Step accuracy reflect real positional accuracy, the higher the step accuracy, the higher the printing quality. Temperature rise – it is the same as mentioned above. Vibration – stepper motor run at a low speed of 100-200mm/s, equal to 50-100RPM in a printer, may have a higher vibration and will affect printing quality. Using a micro-step driver or adding a damper on the stepper motor will help to reduce vibration. As a result of replacing the existing extruder stepper motor on the i3 MK3 with MOONS' MS17HD2P4100, the Prusa (the 3D printing company) website states that MOONS' motors are quieter and cooler and produce more torque for the same amount of current. Given the issues with extruder heat creep, replacing the extruder motor only would be the best "bang for the buck". Thank you Prusa for conducting the test and informing people about MOONS' motor. (https://github.com/PrusaOwners/prusaowners/blob/master/Moons_stepper_motors.md) We, MOONS', would like to recommend the following motors to help improve printing quality.
MOONS' MS17HD2P4100 has a holding torque of 0.48Nm at a motor size of NEMA17, which requires a lower-rated current. Resolution – resolution means the minimum turning angle that a stepper motor can reach, which is called Step-Angle. The most commonly used Step angles are 1.8 degrees and 0.9 degrees. In order to improve resolution, micro-step can be used with a micro-step driver. Micro-stepping refers to the ability to control filament movement in very small increments, thus improving the quality of printing. Step Accuracy — Step accuracy reflect real positional accuracy, the higher the step accuracy, the higher the printing quality. Temperature rise – it is the same as mentioned above. Vibration – stepper motor run at a low speed of 100-200mm/s, equal to 50-100RPM in a printer, may have a higher vibration and will affect printing quality. Using a micro-step driver or adding a damper on the stepper motor will help to reduce vibration. As a result of replacing the existing extruder stepper motor on the i3 MK3 with MOONS' MS17HD2P4100, the Prusa (the 3D printing company) website states that MOONS' motors are quieter and cooler and produce more torque for the same amount of current. Given the issues with extruder heat creep, replacing the extruder motor only would be the best "bang for the buck". Thank you Prusa for conducting the test and informing people about MOONS' motor. (https://github.com/PrusaOwners/prusaowners/blob/master/Moons_stepper_motors.md) We, MOONS', would like to recommend the following motors to help improve printing quality.
 Stepper motor can affect printing quality in a number of ways. ● Holding torque
Stepper motor can affect printing quality in a number of ways. ● Holding torque● Resolution
● Step Accuracy
● Temperature rise
● Vibration Holding torque – normally, stepper motors with higher holding torque have a higher working torque at low speed. Having a higher working torque can ensure sufficient power to pull the filament spool and feed the filament without delay into the extruder. Holding torque – it can lock the position of the extruder during intervals of the printing process. The higher the holding torque, the less likely it is that a small gap will appear at the start of each layer of the print.
 Obtaining a stepper motor with a higher holding torque is not difficult. Several stepper motors have higher holding torque, but they achieve this by increasing the motor size or increasing the current. A larger motor size will result in a larger extruder, and a higher current will result in a higher temperature rise in the clod end, which requires more cooling capacity. MOONS' brand differs from other brands in the following ways:
Obtaining a stepper motor with a higher holding torque is not difficult. Several stepper motors have higher holding torque, but they achieve this by increasing the motor size or increasing the current. A larger motor size will result in a larger extruder, and a higher current will result in a higher temperature rise in the clod end, which requires more cooling capacity. MOONS' brand differs from other brands in the following ways: 
 MOONS' MS17HD2P4100 has a holding torque of 0.48Nm at a motor size of NEMA17, which requires a lower-rated current. Resolution – resolution means the minimum turning angle that a stepper motor can reach, which is called Step-Angle. The most commonly used Step angles are 1.8 degrees and 0.9 degrees. In order to improve resolution, micro-step can be used with a micro-step driver. Micro-stepping refers to the ability to control filament movement in very small increments, thus improving the quality of printing. Step Accuracy — Step accuracy reflect real positional accuracy, the higher the step accuracy, the higher the printing quality. Temperature rise – it is the same as mentioned above. Vibration – stepper motor run at a low speed of 100-200mm/s, equal to 50-100RPM in a printer, may have a higher vibration and will affect printing quality. Using a micro-step driver or adding a damper on the stepper motor will help to reduce vibration. As a result of replacing the existing extruder stepper motor on the i3 MK3 with MOONS' MS17HD2P4100, the Prusa (the 3D printing company) website states that MOONS' motors are quieter and cooler and produce more torque for the same amount of current. Given the issues with extruder heat creep, replacing the extruder motor only would be the best "bang for the buck". Thank you Prusa for conducting the test and informing people about MOONS' motor. (https://github.com/PrusaOwners/prusaowners/blob/master/Moons_stepper_motors.md) We, MOONS', would like to recommend the following motors to help improve printing quality.
MOONS' MS17HD2P4100 has a holding torque of 0.48Nm at a motor size of NEMA17, which requires a lower-rated current. Resolution – resolution means the minimum turning angle that a stepper motor can reach, which is called Step-Angle. The most commonly used Step angles are 1.8 degrees and 0.9 degrees. In order to improve resolution, micro-step can be used with a micro-step driver. Micro-stepping refers to the ability to control filament movement in very small increments, thus improving the quality of printing. Step Accuracy — Step accuracy reflect real positional accuracy, the higher the step accuracy, the higher the printing quality. Temperature rise – it is the same as mentioned above. Vibration – stepper motor run at a low speed of 100-200mm/s, equal to 50-100RPM in a printer, may have a higher vibration and will affect printing quality. Using a micro-step driver or adding a damper on the stepper motor will help to reduce vibration. As a result of replacing the existing extruder stepper motor on the i3 MK3 with MOONS' MS17HD2P4100, the Prusa (the 3D printing company) website states that MOONS' motors are quieter and cooler and produce more torque for the same amount of current. Given the issues with extruder heat creep, replacing the extruder motor only would be the best "bang for the buck". Thank you Prusa for conducting the test and informing people about MOONS' motor. (https://github.com/PrusaOwners/prusaowners/blob/master/Moons_stepper_motors.md) We, MOONS', would like to recommend the following motors to help improve printing quality. | Brand | Model | Holding Torque | Rated Current | Frame Size | Step Angle | Phase | Motor Length |
| MOONS' | MS17HD2P4100 | 0.48Nm | 1A | NEMA 17 | 1.8° | 2 | 39.8mm |
| MOONS' | MS17HA2P4100 | 0.39Nm | 1A | NEMA 17 | 0.9° | 2 | 39.8mm |
| MOONS' | MS17HD6P4100 | 0.63Nm | 1A | NEMA 17 | 1.8° | 2 | 48.3mm |
| MOONS' | MS17HA6P4100 | 0.53Nm | 1A | NEMA 17 | 0.9° | 2 | 48.3mm |
| MOONS' | 17HC6003N | 0.46Nm | 0.82A | NEMA 17 | 1.2° | 3 | 43mm |
| MOONS' | ML24HC4P3150 | 0.72Nm | 1.5A | NEMA 24 | 1.2° | 3 | 45mm |
