Structure of BLDC motor
Brushless DC motor (BLDC) is a type of synchronous motor in which the magnetic fields generated by the stator and rotor are synchronized at the same frequency. BLDC motors operate through an electronic commutator, allowing for continuous and efficient motion. It is widely used due to its high output power, low electrical noise, high reliability, rapid dynamic response, minimal electromagnetic interference, and superior speed-torque performance. These attributes make BLDC motors essential in high-performance applications such as electric vehicles, industrial automation, medical equipment. brushless DC motors play an important role. High output power enables it to meet the demands of high-power equipment, while low electrical noise ensures a quieter working environment. Their high reliability supports stable and consistent equipment operation, and their dynamic responsiveness enables swift adaptation to varying operating conditions. Furthermore, reduced electromagnetic interference minimizes disruption to surrounding electronics, and enhanced speed-torque characteristics ensure efficient performance across a range of load conditions. There are various types of brushless DC motors with different structures; however, fundamentally, a brushless motor system consists of a rotor, a stator, and a motor control unit. The rotor is primarily including permanent magnets, while the stator is composed of coil windings and iron cores. The motor control unit comprises phase commutation and phase detection components, along with a brushless motor controller. The rotor of a brushless DC motor can be classified into two types: outer rotor and inner rotor. The rotor may be equipped with multi-pole block magnets or ring magnets, while the stator poles contain windings. Position detection elements are strategically placed on the stator to work in tandem with the controller, enabling the motor’s commutation. Currently, hall elements are commonly used for this purpose, though other methods for commutation control are also available. Excluding the electronic commutation component, the structure of a brushless DC motor is remarkably simple, making it fully comparable to that of an AC synchronous motor in this regard. 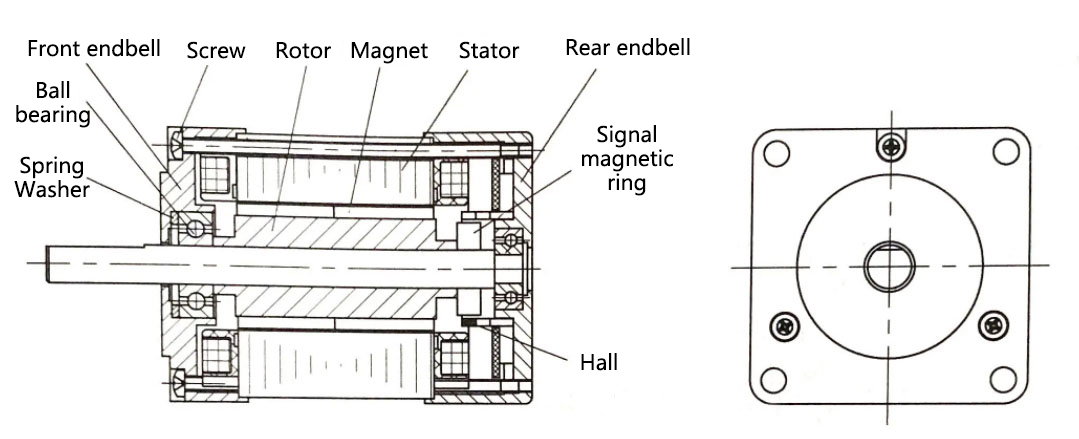 The figure below illustrates the inner rotor structure of a brushless DC motor. This type of motor is widely used across various fields. For instance, in devices with strict space constraints, the inner rotor brushless DC motor is particularly suited to meet design requirements. Additionally, its relatively simple structure provides certain advantages in terms of manufacturing and maintenance.
The figure below illustrates the inner rotor structure of a brushless DC motor. This type of motor is widely used across various fields. For instance, in devices with strict space constraints, the inner rotor brushless DC motor is particularly suited to meet design requirements. Additionally, its relatively simple structure provides certain advantages in terms of manufacturing and maintenance.
 The figure below illustrates the inner rotor structure of a brushless DC motor. This type of motor is widely used across various fields. For instance, in devices with strict space constraints, the inner rotor brushless DC motor is particularly suited to meet design requirements. Additionally, its relatively simple structure provides certain advantages in terms of manufacturing and maintenance.
The figure below illustrates the inner rotor structure of a brushless DC motor. This type of motor is widely used across various fields. For instance, in devices with strict space constraints, the inner rotor brushless DC motor is particularly suited to meet design requirements. Additionally, its relatively simple structure provides certain advantages in terms of manufacturing and maintenance. 