What are the Features of Hybrid Stepper Motors?
• Precise Positioning ControlA stepper motor rotates with a fixed step angle, like the movement of a clock's second hand. This angle is known as the "basic step angle." MOONS' offers several standard motors with different basic step angles: 2-phase stepping motors with a basic step angle of 0.9° and 1.8° and 3-phase stepping motors with a basic step angle of 1.2°. In addition to these standard motors, MOONS' also provides stepper motors with other basic step angles, including 0.72°, 1.5°, 3.6°, and 3.75°. These motors are not listed in this catalog, please contact MOONS' for details.• Easy Control with Pulse SignalsThe following is a system configuration for high-precision positioning. The pulse signals from the controller enable precise control over the rotation angle and speed of the stepper motor. | 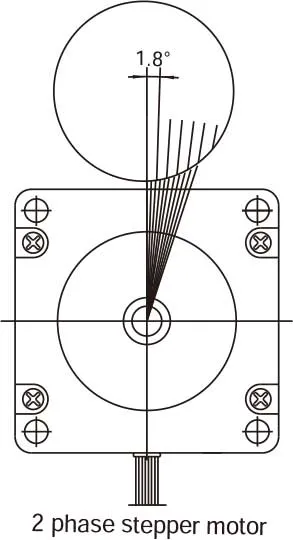 |
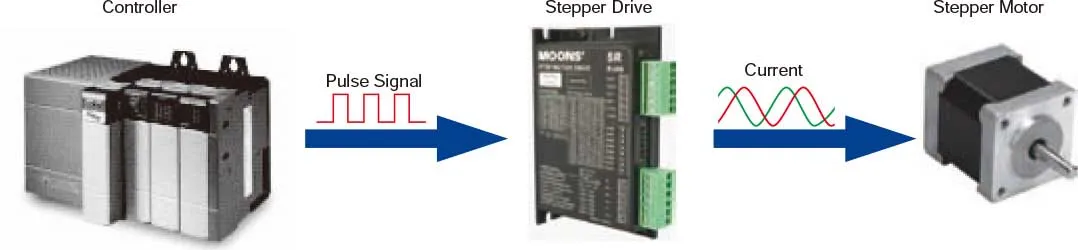 • What is a Pulse Signal?
• What is a Pulse Signal? | A pulse signal is an electrical signal with a voltage level alternates repeatedly between ON and OFF states. Each ON/OFF cycle constitutes a single pulse. A one-pulse command moves the motor's output shaft by one step. The signal levels corresponding to the ON and OFF conditions are referred to as "H"and "L", respectively. | 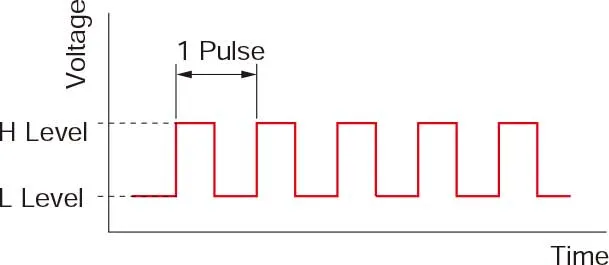 |
| The rotation distance of the stepping motor is directly proportional to the number of pulse signals (pulse count) applied to the driver. The relationship between the stepper motor's rotation (the rotation angle of the motor output shaft) and pulse count is expressed as follows: | 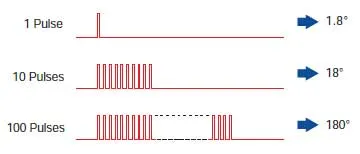 |
 |
| The speed of the stepper motor is proportional to the frequency of pulse signals applied to the driver. The relationship between pulse frequency [Hz] and motor speed [r/min] is expressed as follows: | 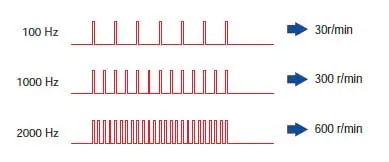 |
 |
• Generating High Torque with a Compact Size
One of the key features of stepper motors is their high torque in a compact form factor. These characteristics provide excellent acceleration and responsiveness, making stepper motors ideal for applications that require frequent starting and stopping. To address the need for higher torque at lower speeds, MOONS' also offers geared motors option.| • Frequent Starting/Stopping is Possible | • Speed VS Torque Characteristics completion between servo and stepper with same motor size. |
 | 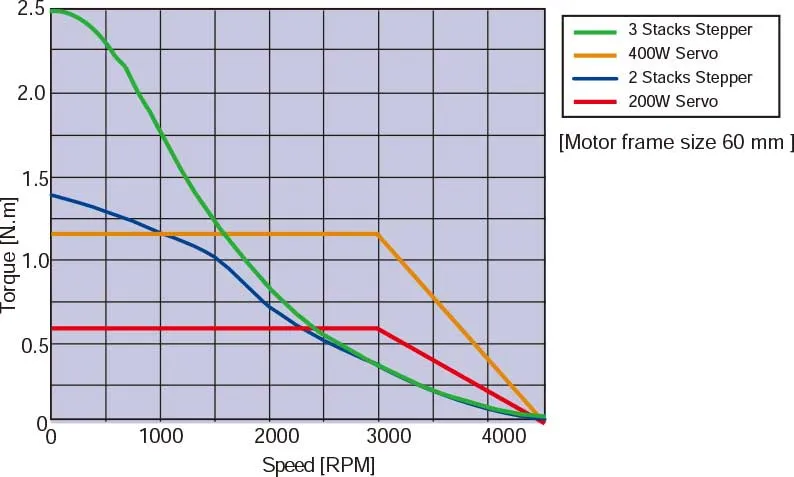 |
• The Motor Holds Itself at a Stopped PositionThe stepper motor maintains full holding torque when its windings are energized, allowing it to remain stationary without the need for a mechanical brake. | 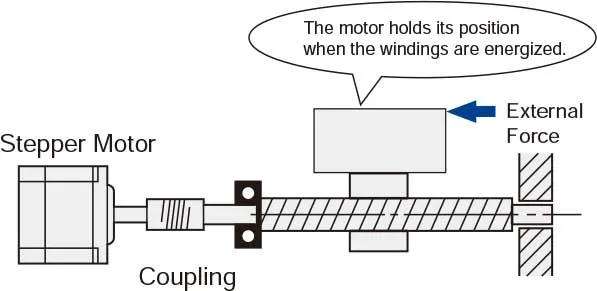 |
• Motor with Electromagnetic BrakeOnce the power is cut off, the motor's self-holding torque is lost, preventing it from remaining in the stopped position during vertical operations or under external force. For lifting and similar applications, a motor equipped with an electromagnetic brake is necessary. | 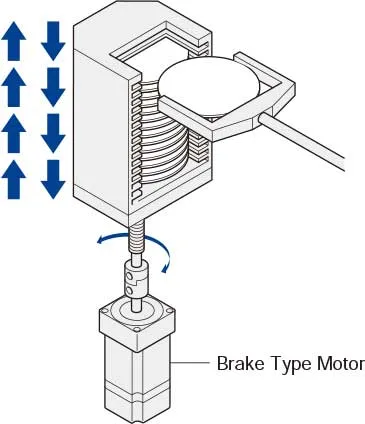 |
• Closed Loop Servo Control Stepper Motors |  |
| The step-servo represents an innovative advancement in stepping motor technology, integrating servo control to deliver a motion control solution with exceptional capabilities. This breakthrough significantly enhances stepping motor performance, offering a more Intelligent, Efficient, Compact, Accurate, Fast, and Smooth. |
