What is the control mode of the DC servo motor?
To understand the control mode of the DC servo motor, you can first look at a set of speed formulas of the DC servo motor: n= (Ua-IaR)/CeФ. Where: Ua is the armature voltage, Ia is the armature current, R is the total resistance of the armature loop, Ce is the EMF constant, and Ф is the magnetic flux of each pole. According to the above speed formula of a DC servo motor, changing the armature voltage Ua and each pole magnetic flux Ф can change the motor speed, so there are two control modes of a DC servo motor: one is armature control, the other is magnetic field control. 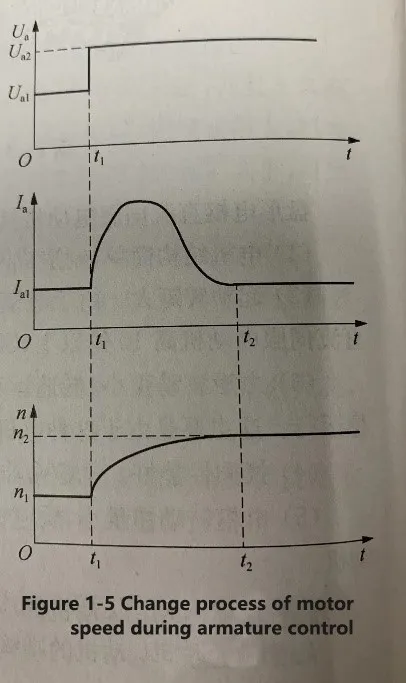 Figure 1-5 Change process of motor speed during armature control
Figure 1-5 Change process of motor speed during armature control
DC servo motor control mode - armature control
The armature control is to keep the excitation flux constant and change the speed of the motor by changing the voltage of the armature winding. When the load torque of the motor is unchanged, increasing the armature voltage, the speed of the motor will increase; Conversely, the speed is reduced; When the armature voltage is equal to zero, the motor does not turn; When the armature voltage changes polarity, the motor reverses. Figure 1-5 illustrates how the motor speed changes under the control of the armature. At t1, the armature voltage of the motor changes from Ua1 to Ua2, the current increases rapidly from Ia1, and the torque increases, so the speed increases from n1. As the speed increases, the back potential increases, the current decreases, and the torque decreases, so the speed is stable. At time t2, the speed stabilizes at a higher speed n2, and the current also returns to Ia1. Figure 1-5 Change process of motor speed during armature control
Figure 1-5 Change process of motor speed during armature control 