5 Undeniable Reasons to Choose this Miniature Stepper Motor
If you're like me, you might be wondering: "With so many types and models of micro motors available, why should I choose a MOONS' motor?"
That's a great question! To address this, let me present you with 5 solid, provable reasons (beyond mere marketing hype) that illustrate why this motor stands out as the choice for you:
That's a great question! To address this, let me present you with 5 solid, provable reasons (beyond mere marketing hype) that illustrate why this motor stands out as the choice for you:
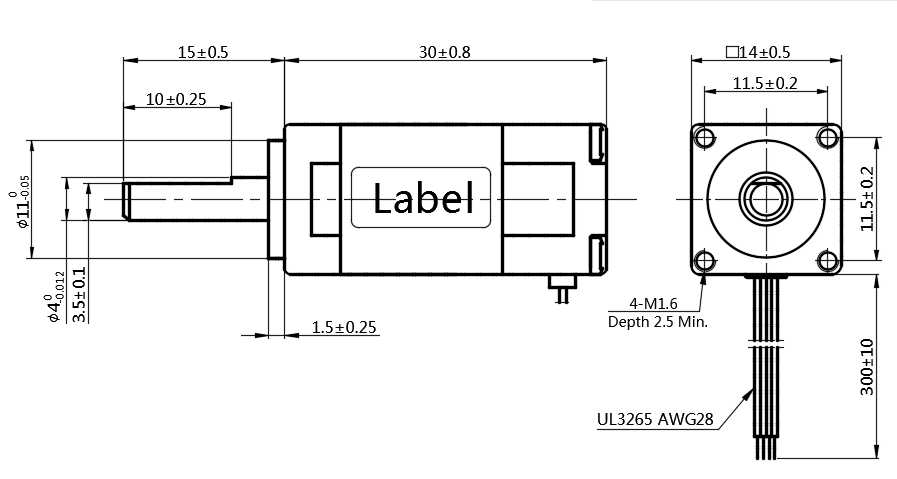
· Reason #1: 14mm×14mm square design, 30mm body length, specially built for applications in small spaces.
Are you grappling with the challenge of finding suitable motors due to the constrained dimensions of your design space? Questioning the viability of your design strategy? Anxious about meeting the dwindling deadlines for your project? This represents a significant leap forward in the realm of hybrid stepper motor body sizes. We understand that reducing the base size below 22mm poses not just a test for the design and manufacture of each component but also challenges the assembly process, the demands on performance, and, critically, serves as a measure of a manufacturer's overall production capability. The innovative 14mm×14mm end face dimension and 30mm hollow body design not only fulfill performance criteria but also maximize space efficiency within your application. This development underscores our commitment to advancing in areas where space savings are paramount, ensuring that our motors integrate seamlessly into your sophisticated designs. | 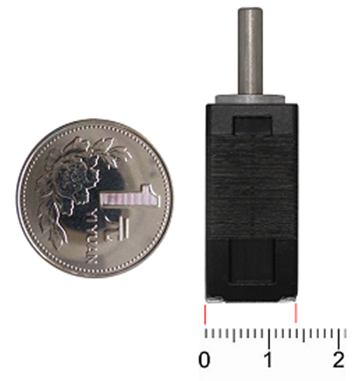 |
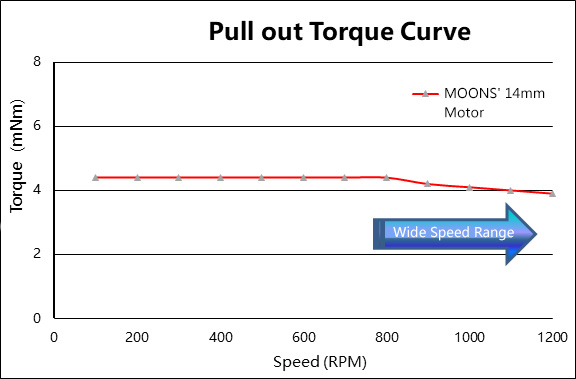
· The hollow structure design of the fuselage greatly increases the winding space, more windings with high fill for more torque.
R&D engineers have been tirelessly innovating to enhance the operating torque, a critical feature of stepper motors. Traditional end cap designs limit the available space for stator windings. Insufficient winding space inevitably weakens the stator's magnetic interaction with the rotor, leading to reduced torque that fails to meet design specifications. By adopting a hollow body structure, the design significantly expands the winding space. This increase allows for a higher fill rate of windings, thereby boosting the output torque and ensuring the motor meets, if not exceeds, design expectations.
 |  |
· Reason #3: Low inertia for easier starting.
Rotational inertia quantifies the resistance of a rigid body to changes in its rotational motion, depending on both the mass of the body and how that mass is distributed relative to the rotation axis. It essentially measures an object's inertia against rotational movement. The 14H030H micro stepper motor boasts a remarkably low moment of inertia of just 0.5g•cm², facilitating easier and quicker starts.
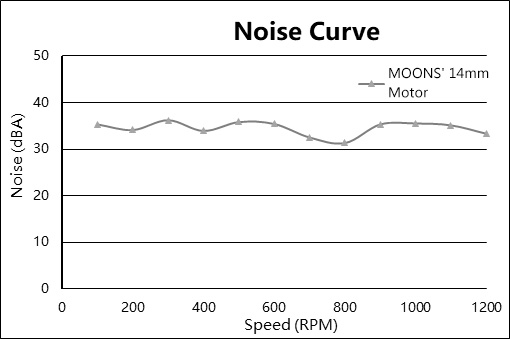
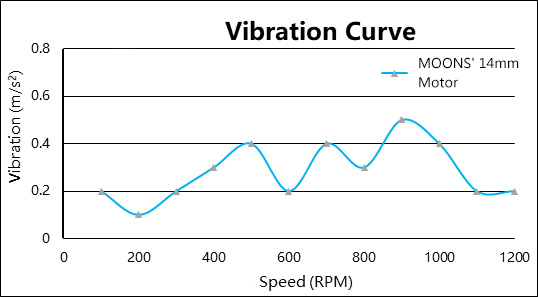
· Reason #4: Less noise, more quiet.
The vibration and noise associated with the motor body can stem from several factors, including cogging torque; insufficient rigidity of the stator and end cap; imbalance in the coil and magnetic circuit, asymmetry in mechanical structure; and issues with rotor eccentricity or poor dynamic balancing. The 14H030H micro stepper motor leverages its multifaceted advantages to keep operating noise below 40dBA, ensuring a serene and noise-free application environment for users.
 |  |
· Reason #5: Wide range of customizable options to choose.
 | 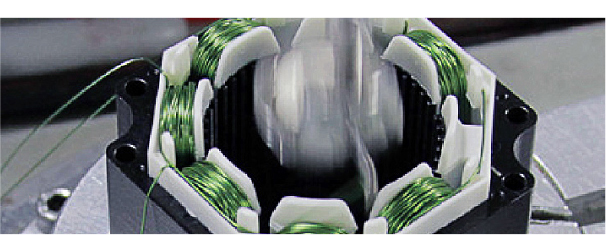 | 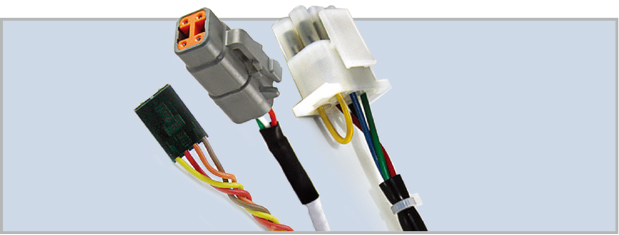 | ||
We offer many different shaft options for your motor as well as customizable shaft lengths to make the motor fit your application seamlessly. | Hybrid Stepper Motor's winding can be optimized in a variety of ways to ensure optimal performance within your application. | Utilize our in-house wiring and wire-harness manufacturing capabilities to customize the wiring and cabling to your exact specifications. |
Specification
| Model | Holding Torque | Length | Step Angle | Step Accuracy | Phase | Rated Current | Resistance (±10% @ 20°C) | Inductance (±20%) | Rotor Inertia (Typ.) | Detent Torque (Typ.) | Number of Leads | Motor Weight (typ.) |
| 14H030H-0304 | 5.8mNm | 30mm | 1.8° | ± 5% | 2 | 0.3 A | 22 Ω | 43.8mH | 0.5g. cm² | 0.7mNm | 4 | 30 g |
Motor Dimensions: mm