MOONS' TRS/TRV Series Vibration Damping Rotor Stepper Motors
1. Overview of stepper motors
Hybrid stepper motors are pulse-controlled precision motors. Its control accuracy is generally within ±5% of the step angle. Suitable for open-loop applications requiring high positional accuracy, it is ideal for open-loop applications. In general, stepper motors operate in an open-loop configuration. During operation, the motor's speed is unstable. There will be an obvious resonance zone at low speeds and a long-term position jitter when the motor stops. The application scope of stepper motors is constrained due to their unstable operation and the jitter experienced upon stopping. 2. Universal vibration reduction method for stepper motors
In order to solve the problem of low-speed vibration and jitter when the stepper motor stops, there are currently two methods in the industry: Method 1:
Add stator vibration damping parts to the motor stator to isolate the vibration of the motor stator from being transmitted to the installation mechanism to a certain extent. 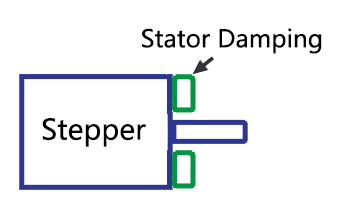 Method 1: Stator Damping
Method 1: Stator Damping Method 2:
Install a rotor vibration damper at the outlet end of the motor rotor to reduce the load vibration caused by the vibration of the motor rotor. 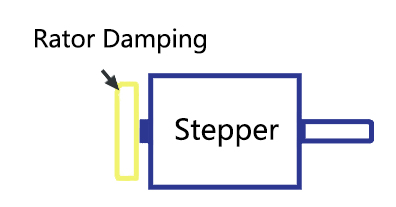 Method 2: Rotor Damping The stator vibration reduction method effectively isolates stator vibrations, mitigating their impact on the installation structure. However, much of the vibration is transmitted directly to the load through the rotor, resulting in load vibration. The rotor vibration damping method reduces load vibration caused by rotor vibration. However, external rotor damping components increase the motor's thickness, impacting its installation space. This makes it unsuitable for applications that have stringent size constraints or require motors with double output shafts.
Method 2: Rotor Damping The stator vibration reduction method effectively isolates stator vibrations, mitigating their impact on the installation structure. However, much of the vibration is transmitted directly to the load through the rotor, resulting in load vibration. The rotor vibration damping method reduces load vibration caused by rotor vibration. However, external rotor damping components increase the motor's thickness, impacting its installation space. This makes it unsuitable for applications that have stringent size constraints or require motors with double output shafts.3. MOONS' TRS/TRV series vibration damping rotor stepper motor principle
MOONS' newly developed TRS/TRV series of vibration-damped rotor stepper motors feature rotor vibration-damping components integrated within the stepper motor's rotor. This design retains all the benefits of existing rotor vibration damping methods while offering additional advantages: 1) The motor's torque remains largely unaffected. 2) There is no change in the motor's axial dimensions. 3) The design is suitable for applications requiring double output shaft motors and those with strict size specifications. 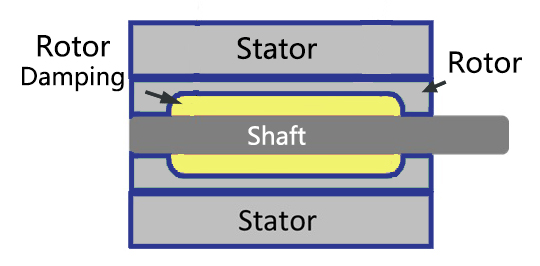 MOONS' vibration damping rotor stepper motor principle
MOONS' vibration damping rotor stepper motor principle4. MOONS' TRS/TRV series vibration damping rotor stepper motor effect
Compared to conventional motors, vibration-damped rotor stepper motors exhibit significant improvements in single-frequency response time and speed ripple. In terms of single-frequency response time, the stabilization time of the vibration-damped rotor motor is reduced to half that of conventional motors. When considering the speed fluctuations during operation, the vibration-damped rotor motor exhibits significantly reduced speed variations in its rotor compared to conventional motors. Apart from at low speeds, it experiences almost no major speed changes. The reduction in positioning time is highly advantageous for applications requiring rapid motor start-stop cycles, like testing in the semiconductor industry. A stable running speed, sought after in virtually all applications, makes it particularly well-suited for light-load uses such as fly-by photography and videography. The significant enhancements in positioning time reduction and operating speed stability enable two-phase stepper motors to rival the characteristics of multi-phase small step angle stepper motors. Additionally, the speed and torque range of the two-phase vibration-damped rotor stepper motor is far superior to that of multi-phase small step angle stepper motors. 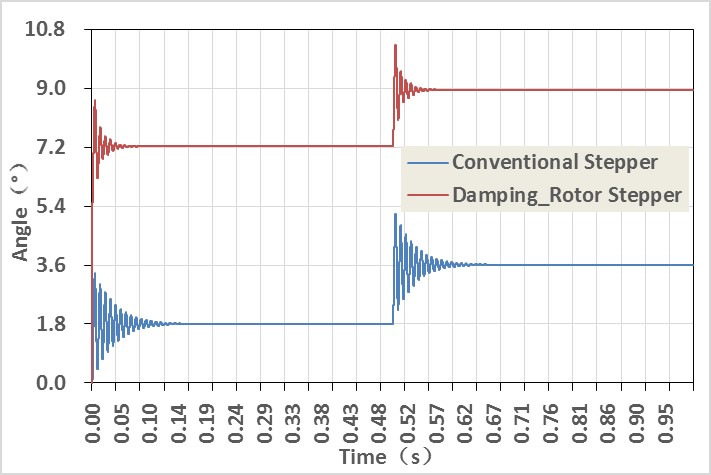 Comparison of response time of two-phase conventional motor and vibration-damped rotor motor
Comparison of response time of two-phase conventional motor and vibration-damped rotor motor 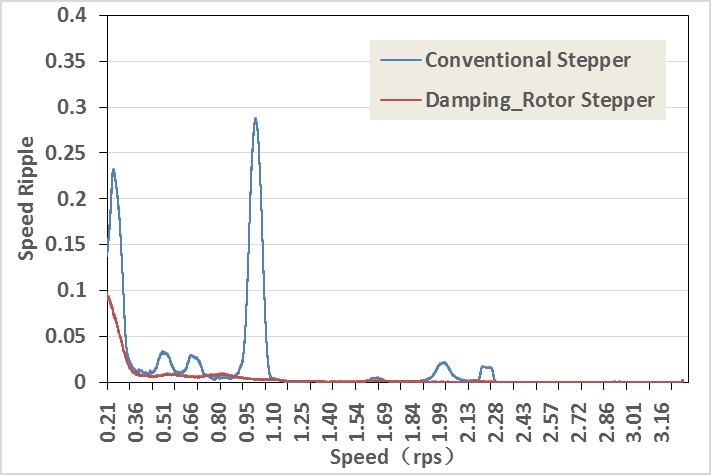 Comparison of speed changes during operation of two-phase conventional motor and vibration-damped rotor motor
Comparison of speed changes during operation of two-phase conventional motor and vibration-damped rotor motor5. TRS/TRV motor specifications
Two-phase and three-phase motors of Nema17 and above can use vibration-damped rotor motor technology.